Pasteurization is a cornerstone of contemporary meals security.
Pasteurization performs a crucial function in stopping foodborne diseases.
Developed within the nineteenth century, this course of includes heating meals to a selected temperature to kill dangerous microbes, then quickly cooling it to forestall spoilage. It is particularly important for merchandise like milk, beer, juice, meats, and extra.
Earlier than we dive in, don’t overlook to obtain our pasteurization temperature chart for fast reference.
Key factors coated:
-
Pasteurization is a course of that heats meals to a selected temperature for a set time after which cooling it so as to kill dangerous pathogens.
-
French scientist Louis Pasteur is named the daddy of pasteurization.
- Three key steps of the pasteurization course of are heating, usually from 145°F (63°C) to 275°F (135°C); holding the meals or beverage at a temperature for a set time to kill dangerous microbes; and cooling or chilling to forestall remaining micro organism from multiplying.
- Pasteurization is efficient towards many dangerous micro organism, together with Salmonella, E. coli, Listeria, ampylobacter, and Mycobacterium bovis.
- 4 sorts of pasteurization embody Vat Pasteurization, Excessive-Temperature Quick Time (HTST) Pasteurization, Greater-Warmth Shorter Time (HHST) Pasteurization, and Extremely-Excessive Temperature (UHT) Pasteurization.
-
FoodDocs’ digital Meals Security Administration System might help meals producers who do pasteurization simply monitor and hint their merchandise! implement their meals security plan and keep compliance with it!
What’s pasteurization?
Pasteurization is a course of that heats meals (usually liquids like milk, juice, and beer) to a selected temperature for a set time. This kills dangerous microbes and prevents spoilage. The meals is then quickly cooled to keep up its freshness.
Although it does not sterilize the meals fully, it does considerably cut back the chance of foodborne sickness, making it safer for consumption.
Who invented pasteurization?
Louis Pasteur, a French scientist, is the daddy of pasteurization. Within the mid-1800s, Pasteur developed this course of whereas finding out find out how to forestall spoilage in wine and beer. His work laid the inspiration for contemporary meals security practices.
The time period “pasteurization” itself is a tribute to his groundbreaking contribution.

Pasteurized vs unpasteurized
Pasteurization is a course of designed to kill dangerous micro organism in meals, whereas unpasteurized merchandise skip this step, providing a unique set of dangers and advantages.
Under, we break down the variations between pasteurized and unpasteurized meals by way of security, shelf life, dietary content material, and taste.
Pasteurized merchandise:
- Security: Pasteurization considerably reduces the presence of dangerous micro organism like Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria, making the meals safer to eat.
- Shelf life: These merchandise usually have longer shelf life dates because of the discount of spoilage-causing, dangerous microorganisms.
- Dietary content material: Whereas some imagine pasteurization reduces dietary content material, the loss is minimal and outweighed by the protection advantages.
- Taste: The method can barely alter the style, although trendy strategies intention to protect the unique taste as a lot as attainable.
Unpasteurized merchandise:
- Security: Meals equivalent to unpasteurized milk carry a better threat of containing dangerous micro organism, which may result in foodborne diseases.
- Shelf life: These merchandise typically have a shorter shelf life, because the pure micro organism and enzymes are nonetheless energetic.
- Dietary content material: Some argue that unpasteurized merchandise retain extra of their pure vitamins and enzymes.
- Taste: Many individuals want the style of unpasteurized merchandise, which may be richer and extra advanced because of the presence of pure microbes.
Right here’s a side-by-side comparability of pasteurized vs unpasteurized to spotlight the important thing variations:
| Characteristic | Pasteurized | Unpasteurized |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Low threat of dangerous micro organism | Greater threat of dangerous micro organism |
| Shelf life | Longer because of diminished spoilage | Shorter, as pure microbes are nonetheless energetic |
| Dietary content material | Barely diminished, however minimal impression | Probably retains extra pure vitamins |
| Taste | Slight alteration, however typically preserved | Usually richer, extra advanced because of pure microbes |

What are the three steps within the pasteurization course of?
The pasteurization course of typically includes three key steps:
- Heating: The meals is heated to a selected temperature. This varies relying on the kind of pasteurization however usually ranges from 145°F (63°C) to 275°F (135°C).
- Holding: The meals is held at this temperature for a set time, guaranteeing that dangerous microbes are successfully killed.
- Cooling: Often known as the chilling stage, the meals is quickly cooled to forestall any remaining micro organism from multiplying.
This three-step course of is crucial in guaranteeing that meals stays protected with out compromising its high quality. That stated, there are sorts of pasteurization (which we cowl in a few paragraphs) that do drastically alter qualities equivalent to nutrient density and taste.
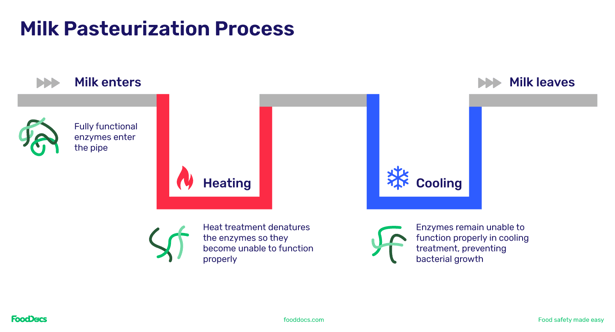
People within the meals security business generally embody 5 extra steps main as much as the three key pasteurization steps we listed above. Utilizing milk for instance:
- Chilling: Technically not a part of the pasteurization course of, chilling is useful when working with milk in giant volumes. It is because if you first get milk from a cow, the temperature is above ambient which will increase the chance of bacterial spoilage. Decreasing temperatures to between 35.6°F and 41°F (2°C and 5°C) helps cease the expansion of micro organism.
- Pre-heating: Additionally known as regeneration, you warmth the chilled milk to ~104°F to to make the separation of butterfat throughout standardization simpler.
- Clarification: This a part of the method helps take away overseas matter from the milk product, normally through the use of metallic filter tubes to pressure the milk.
- Standardization: Folks want to eat various kinds of milk (e.g., skim, low-fat, high-fat). Standardizing milk fats fats helps be certain that no matter sorts of merchandise you are producing are constant in high quality.
- Homogenization: Throughout this course of, milk fats globules are damaged down into tiny droplets of fats in order that the cream is much less prone to separate. This helps preserve the milk’s fats evenly distributed.
What micro organism are killed by by pasteurization?
Pasteurization is efficient towards many dangerous micro organism, together with Salmonella, E. coli, Listeria, ampylobacter, and Mycobacterium bovis. These harmful pathogens are accountable for severe foodborne diseases, and pasteurization considerably reduces their presence in meals.
A current observational examine of 48 human milk samples discovered that “holder” and “flash” pasteurization strategies confirmed important discount in E. coli progress to 46.4% and 25.5 per cent, respectively.”
The outcomes help the concept pasteurization remains to be one of the dependable strategies for controlling these micro organism in juice and dairy merchandise.
In response to the Centre for Meals Security:
Pasteurization methods are developed to attain a 99.999% discount of the microbial load through the use of essentially the most heat-tolerant goal pathogen Coxiella burnetii. The upper temperature is utilized, the shorter the warmth remedy time is required. The pasteurisation time and temperature combos used are designed for killing dangerous micro organism.
Which micro organism will not be killed by pasteurization?
Whereas pasteurization is very efficient, it does not kill all micro organism. Sure heat-resistant spores, equivalent to these from Clostridium botulinum, can survive the method.
In the identical useful resource above, meals security specialists acknowledge that “pasteurization has its limitations. Some spore-forming micro organism like Bacillus might stay energetic after pasteurization, which may result in meals spoilage and even meals poisoning if the pasteurized meals is saved below improper circumstances.”
Nevertheless, these spores are typically not dangerous until the meals is wrongly saved, which may enable them to develop. This highlights the significance of correct meals dealing with even after pasteurization.

4 Forms of pasteurization
There are a number of sorts of pasteurization, every with its personal temperature and time necessities:
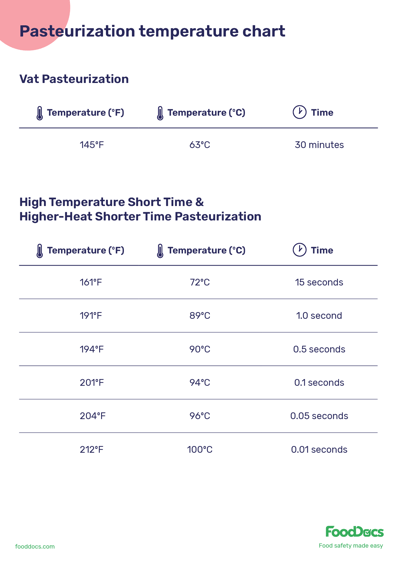
- Vat Pasteurization: Heating meals to 145°F (63°C) for half-hour. Generally used for milk. It is often known as Low-Temperature Lengthy Time (LTLT) pasteurization.
- Excessive-Temperature Quick Time (HTST) Pasteurization: Heating to 161°F (72°C) for 15 seconds. That is the commonest methodology for milk and fruit juice.
- Greater-Warmth Shorter Time (HHST) Pasteurization: Just like HTST however at increased temperatures, usually 192-212°F (89-100°C) for a number of seconds.
- Extremely-Excessive Temperature (UHT) Pasteurization: Heating to 275°F (135°C) for 2-5 seconds. Used for merchandise needing an extended refrigerated shelf life, like cream and milk.
In “Handbook of Farm, Dairy and Meals Equipment Engineering“, authors write:
In comparison with sterilization, pasteurizing is a relatively low order of warmth remedy, typically at a temperature beneath the boiling level of water. The final goal of pasteurization is to increase product shelf-life by inactivating all non-spore-forming pathogenic micro organism and nearly all of vegetative spoilage microorganisms, in addition to inhibiting or stopping microbial and enzyme exercise. To be efficient, pasteurization is regularly mixed with one other technique of preservation equivalent to focus, acidification, chemical inhibition, and many others.
5 Hottest pasteurized meals
Strategies for the preferred pasteurized meals embody:
- Milk: Pasteurized primarily utilizing HTST at 161°F (72°C) for 15 seconds.
- Eggs: Usually pasteurized of their shells at round 140°F (60°C) for 3.5 minutes.
- Juice: Pasteurized utilizing HTST or UP strategies, relying on shelf-life necessities.
- Hen: Hardly ever pasteurized, however some processes use temperatures round 158°F (70°C) for a number of seconds.
- Beer: Flash pasteurized at 140-158°F (60-70°C) for a short while to keep up taste.
Pasteurization temperature chart
Discuss with our common pasteurization temperature chart for an in depth breakdown of inner temperature time combos. You may as well obtain the chart for simple entry throughout your meals security operations.
Try our different food-specific pasteurization temperature charts, which you’ll be able to obtain at no cost:
Learn how to use meals security software program for simple monitoring throughout pasteurization
When you work within the dairy business or one other a part of the meals manufacturing business that pasteurizes meals, take a look at FoodDocs’ Meals Security Administration software program.
It makes monitoring temperatures — scorching, chilly, and all the things in between — easier and correct. Along with each day pasteurization temperature logs, the meals security monitoring system additionally consists of cleaning checklists (for pasteurization tanks), receiving logs (for traceability), and extra!
- Good notifications: Temperatures which are out of the appropriate vary through the pasteurization course of will attain your related workforce members immediately. They’re going to be capable to full the instructed corrective actions in accordance with your organization’s requirements, to allow them to keep away from meals security incidents and keep compliant.
- Batch-based monitoring with traceability: Full traceability logs and connect monitoring duties to the identical pasteurized product batch immediately. Log scorching or chilly temperature checks to the ready batch through the preparation course of. This ensures crucial traceability and visibility in case of a recall or buyer criticism and can enable you to guarantee high-quality meals security.
- Management by verifying duties: You’ll be able to select to confirm the monitoring job entries. Assign it to your self or a supervising workforce member to make sure that your employees full their pasteurization-related actions in accordance with meals security necessities.
Digitize your meals security system with FoodDocs and begin your 14-day free trial at the moment!
FAQs about pasteurization
Listed below are some widespread questions associated to pasteurization:
What’s killed by pasteurization?
Pasteurization kills dangerous micro organism like Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria.
What’s pasteurization at 72 levels Celsius?
This refers to Excessive-Temperature Quick Time or HTST pasteurization, the place meals is heated to 161°F (72°C) for 15 seconds.
What’s the authorized temperature for pasteurization?
The authorized temperature varies by product however is commonly 161°F (72°C) for pasteurized milk.
Why is the temperature of pasteurization at 60 levels Celsius?
Some meals, like egg merchandise, are pasteurized at decrease temperatures to forestall coagulation whereas killing micro organism.
How do they pasteurize milk?
Milk is often pasteurized utilizing the HTST methodology, heated to 161°F (72°C) for 15 seconds.
Is pasteurization meals protected?
Sure, pasteurization is a confirmed methodology for decreasing foodborne ailments.
What’s the pasteurization course of?
The pasteurization course of includes heating meals to a selected temperature to kill dangerous microbes after which quickly cooling it.
Why are folks towards pasteurization?
Some folks imagine pasteurization reduces the dietary high quality of meals, although that is largely debunked. Regardless, Canada prohibits the sale of uncooked milk merchandise. Within the U.S., 30 states enable the sale of uncooked milk whereas 20 states explicitly prohibit it.
Is pasteurization simply boiling?
No, pasteurization makes use of managed temperatures which are decrease than boiling to kill microbes with out affecting meals high quality.